
MPO / MTP fiber breakout/fan-out cable means that after processing the MPO/MTP connector and the optical fiber cable, with Optical Branching Device, one end is an MPO/MTP connector, and the other end can be matched with a variety of connectors such as LC/SC/FC (LC the most widely used). The common types are MPO / MTP (8-core) to 4 x LC fiber breakout cable, MPO / MTP (12 core) to 6 x LC fiber breakout cable, and MPO / MTP (24 core) to 12 x LC fiber breakout cable. through cross-type pre-connected MPO/MTP technology, one end is connected to 40G/100G, the other end is connected to 10G, and a 40G/100G is decomposed into several 10G to achieve a high rate port (MTP/MPO) to low Ideal transfer for rate ports (LC/SC/FC). MPO/MTP-LC fiber breakout can be used in many existing DC environments due to their large number of cores, compact design, small size, etc., such as between switches, rack-mounted panels and main distribution wiring boards, etc. .

The Main Advantages of MPO/MTP Fiber Breakout Cables
- MPO/MTP fiber breakout cable provide a neat, high-density method to achieve high-density switch port replication, which can reduce the risk of switch port damage or errors.
- MPO/MTP fiber breakout cable occupies less space in the cabinet and has better vertical management than the traditional fiber optic cable. For example, the MPO/MTP 12-core breakout cable is much smaller than the fiber optic cables with the same number of cores.
- Reduce the inconvenience caused by the congestion of optical cables to the management of local area networks and storage network centers; increase the cooling airflow, making it easier to move/add/change cables or equipment.
- MPO/MTP fiber breakout cable provide interleaved LC breakouts that can be used to include engineering customization to match the network ports of electronic devices to provide seamless integration between wiring infrastructure and electronic devices.
Typical Application of MTP-LC Breakout Cable?
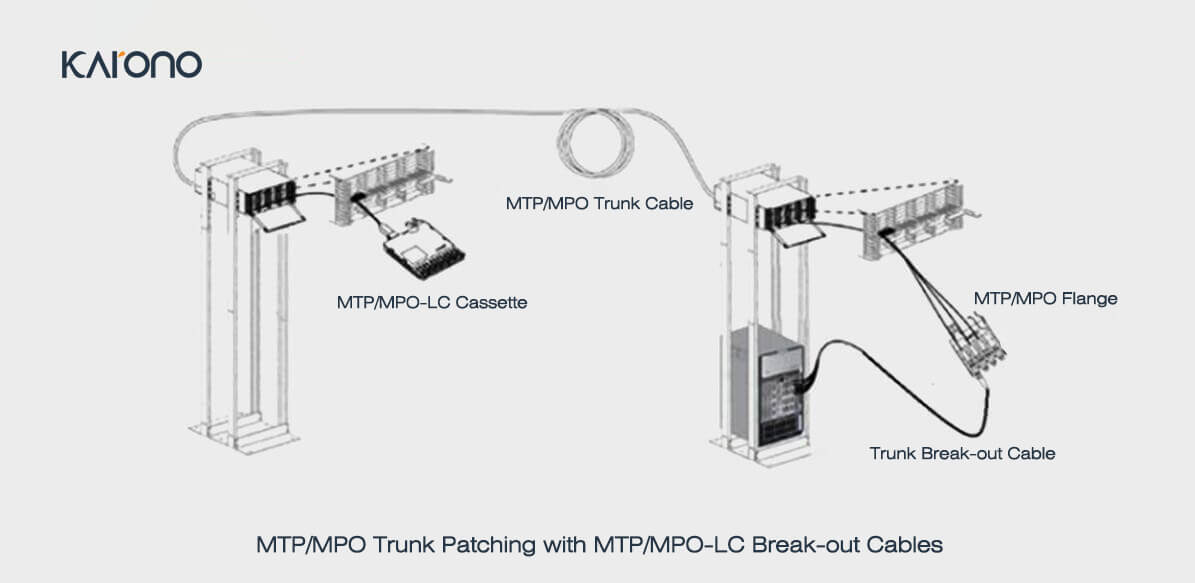
The MTP-LC Breakout Cable is used for port replication of blade switch boards, which facilitates the connection of these ports to other devices. Based on the specific application and what kind of components are inserted, it is divided into two types of branch jumpers, module branch jumpers and trunk branch jumpers.
The module branch jumper is directly connected to the rear of the MTP-LC module, and the switch port is copied to the distribution frame located in the same or adjacent rack. When this application is usually used, the switch is located in the MDA or column header exchange.
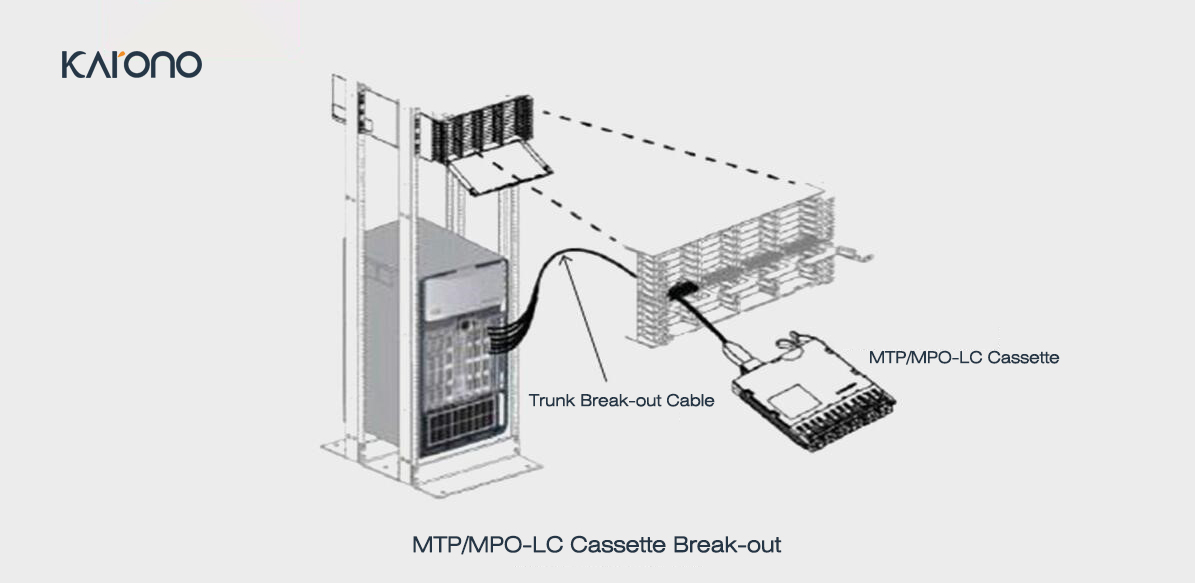
The switch distribution panel is located outside the location where the switch is located. Deploying this application is usually when you have a universal switching area and the main distribution area (MDA) required for port replication.
 EN
EN ES
ES DE
DE